Hardware refers to the physical equipment used for the input, processing, output and storage activities of a computer system. The hardware includes the physical artefacts technology for instance PC’s, printers, mouses, monitors, routers and hard drives.
Hardware consist of many parts such as the Central Processing Unit (CPU): which manipulates data ad controls the tasks performed by other components, Primary storage: internal to the CPU; which stores data and program instructions during processing, Secondary Data: external to the CPU; which stores data and programs for future use; Input Technologies: accepts data and instructions and convert them to a form that the computer can understand; Output Technologies: data and information that people understand and finally; Communication Technologies: provides the flow of data from external computer networks (internet) to the CPU, and CPU to networks.
 2. What is Moore's Law/what does it mean in relation to computers.
2. What is Moore's Law/what does it mean in relation to computers.According to computer narration and its development Moore’s Law is the preeminent way to describe the stages.
Moore's Law - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore
The law explains the continuing change and trends of the computer history. The following changes of Moore’s Law include:
· The increasing miniaturization of transistors,
· Making the physical layout of the of the chip’s component as compressed and efficient as possible,
· Using materials for the chip that improve the flow of electricity, and
· Targeting the amount of basic instructions programmed into the chip.
Thus in relation to computers, It is evident that from the law that the microprocessor complexity would double every two years and as a result from a business perspective this means that over time the price of PC will decrease and the speed will increase. Moore’s Law was constructed in the 1950’s as he was the founder of the Intel computer, thus the conclusion above was derived from the results.
 3. In basic terms, describe how a microprocessor functions.
3. In basic terms, describe how a microprocessor functions.The microprocessor also kn own as the ‘processor’ or ‘central processing unit (CPU)’ performs the actual computation inside any computer e.g. Intel Core Duo. It is the chip that interprets program instructions and process data. It manipulates the data and controls the tasks performed by the other components. As seen in the image the microprocessor is made up of millions of microscopic transistors in a circuit on a silicon chip it consist of:
own as the ‘processor’ or ‘central processing unit (CPU)’ performs the actual computation inside any computer e.g. Intel Core Duo. It is the chip that interprets program instructions and process data. It manipulates the data and controls the tasks performed by the other components. As seen in the image the microprocessor is made up of millions of microscopic transistors in a circuit on a silicon chip it consist of:
 own as the ‘processor’ or ‘central processing unit (CPU)’ performs the actual computation inside any computer e.g. Intel Core Duo. It is the chip that interprets program instructions and process data. It manipulates the data and controls the tasks performed by the other components. As seen in the image the microprocessor is made up of millions of microscopic transistors in a circuit on a silicon chip it consist of:
own as the ‘processor’ or ‘central processing unit (CPU)’ performs the actual computation inside any computer e.g. Intel Core Duo. It is the chip that interprets program instructions and process data. It manipulates the data and controls the tasks performed by the other components. As seen in the image the microprocessor is made up of millions of microscopic transistors in a circuit on a silicon chip it consist of: - Control Unit: accesses program instructions, decodes and controls the flow of data to and from the arithmetic logic unit as it registers primary and secondary storage.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit: performs the mathematical calculations
- Registers: high speed storage that store very small amounts of data and instructions for short periods of time.
Microprocessor Functions: http://au.encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761559091/microprocessor.html
4. What factors determine the speed of the microprocessor?
The factors that determine the speed of the CPU include the clock speed, word length, bus width, and design of the chip however with the assistance of binary form and the machine instruction cycle the microprocessor speed is established. The clock speed in GHz helps to preset the speed of the computer clock, while the word length shows how many characters the PC reacts in one clock cycle, additionally the bus width assists the speed by performance of the amount of data that can travel at the same time finally the line width shows the distance between transistors thus the smaller the line width, the faster the chip.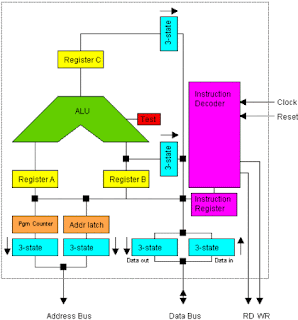
5. What are the four main types of primary storage.
Primary storage: stores small amount of data and information that will be immediately used by the CPU. The four main types include:
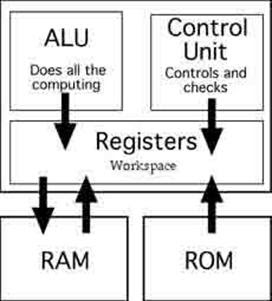
1) Registers: part of the CPU with least capacity, storing little data only immediate before and after processing.
2) Random Access Memory (RAM): holds software and small amount of data when brought from secondary storage.
3) Cache Memory: stores blocks of data used more often.
4) Read Only Memory (ROM): storage is non-volatile thus, retains instructions when the power of the computer is turned off.
6. What are the main types of secondary storage?
Secondary storage: stores much larger amounts of data and information for extended periods of time, four main types of storage include:
1) Magnetic Tape: (Sequential Access) medium storage, large open reel or smaller cartridge or cassette. 

2) Magnetic Disk: (Direct Access) magnetic disk divided into track and sectors provide addresses for various data example include: hard disk.
3) Hard Drives: Platte divided into concentric tracks and sectors; it reads / writes pivots across the rotating disk.
4) Direct Access: any piece of data retrieved anytime located by data’s address.
Secondary Storage - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_data_storage
7. How does primary storage differ from secondary storage in terms of speed cost and capacity?
7. How does primary storage differ from secondary storage in terms of speed cost and capacity?
Primary storage stores small amount of data and information that will be immediately stored on the CPU.
The primary storage stores many types of information for a short time:
§ Data to be processes by the CPU
§ Instructions for the CPU as to how to process the data
§ Operating system programs that manage various aspects of the computer operation.
§ The storage is faster, RAM quickly though more costly.
§ The storage takes place on ‘chips’ on the motherhood.
Secondary storage is the permanent of larger amounts of data. The secondary storage stores many types of information for an extended period of time the storage differs from primary as it:
§ Non volatile
§ Takes much more to retrieve data because of the electromechanical nature
§ Cheaper than primary storage
§ Can be taken place on a variety of media.
§ Storage is moderate, RAM is less costly
§ Storage is moderate, RAM is less costly
The primary and secondary storages differ as primary has faster storage though more costly however has more capacity. Whereas the secondary storage is limited and cheaper though it is reliable as it can be taken everywhere.
8. What are enterprise storage systems?
Enterprise storage systems are independent, external system with intelligence that includes two or more storage devices.
Three types of enterprise storage systems include:
I. Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID): Similar to standard hard drive, it is a specialised microcontroller that coordinates the drive therefore; appears to a single logical drive. II. Storage Area Network (SAN): building special area network, that allows rapid and reliable access to storage devices by multiple servers.
III. Network Attached Storage (NAS): device is a special purpose server that provides file storage to user when access the device over a network.
Enterprise Storage Systems - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_software
9. Distinguish between human data input devices and source data automation.
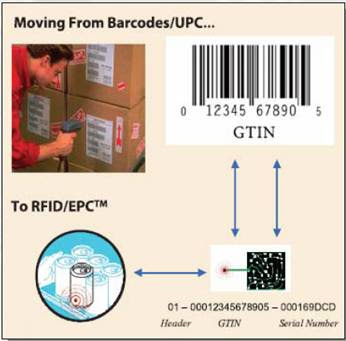 Human Data Entry is when the individual physical penetrates the information and process into the devices; this includes keyboards, optical mouse, trackball, joystick, and webcam. This procedure however takes longer.
Human Data Entry is when the individual physical penetrates the information and process into the devices; this includes keyboards, optical mouse, trackball, joystick, and webcam. This procedure however takes longer.In contrast, the Source-Data Automation Input is the gathering and amending data where it is primarily formed in so that it can be directly input in to the computer as a result indicating accuracy and timeliness. Types of source-data automation include barcodes scanners, Radio frequency identification (RFID), magnetic stripe readers and automated teller machines.
10. What is one new technology that will change how we do things?
Technology is a human innovation in action that involves the generation of knowledge and processes to develop systems that solve problems and extend human capabilities. (www.insme.org/page.asp)
Technology is a human innovation in action that involves the generation of knowledge and processes to develop systems that solve problems and extend human capabilities. (www.insme.org/page.asp)
However, a technology that will change how individuals perform their daily tasks and interaction in the world will be the iPhone.
 With the release of the iPhone towards the end of 2007, the world had discovered a technology that combines three different devices, as it includes the innovative phone, widescreen iPod and advance internet device. With the combination of these three mechanisms, it has produced an efficient, effective, and reliable apparatus that assists the many busy people of the world helping them with their flexibility of time.
With the release of the iPhone towards the end of 2007, the world had discovered a technology that combines three different devices, as it includes the innovative phone, widescreen iPod and advance internet device. With the combination of these three mechanisms, it has produced an efficient, effective, and reliable apparatus that assists the many busy people of the world helping them with their flexibility of time.Nevertheless, the iPhone helps individuals that are always ‘on the go’ to check all their emails, make voice and video calls at any period. Additionally, it has the capability of downloading the latest songs and watching DVDs in the touch of a finger. If those were not enough reasons the iPhone uses the most up-to-date 3G and Wi-Fi connections to deliver all the aspects in web browsing. Therefore, this wireless technology will change the way we perform our daily tasks, as it will allow to multitask many events due to the masses of applications it holds and thus have no need to wait in queues!
iPhone - http://www.apple.com/iphone/why-iphone/
iPhone Specifications - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPhone
iPhone - http://www.apple.com/iphone/why-iphone/
iPhone Specifications - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPhone

No comments:
Post a Comment